Understanding Agents: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Agents: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of artificial intelligence and computer science, the term "agent" holds significant importance. Agents are software entities that perform tasks autonomously on behalf of a user or another program. This article aims to delve deep into the concept of agents, exploring their types, functionalities, and applications. Additionally, we'll touch upon how agents are shaping the future of technology.
What is an Agent?
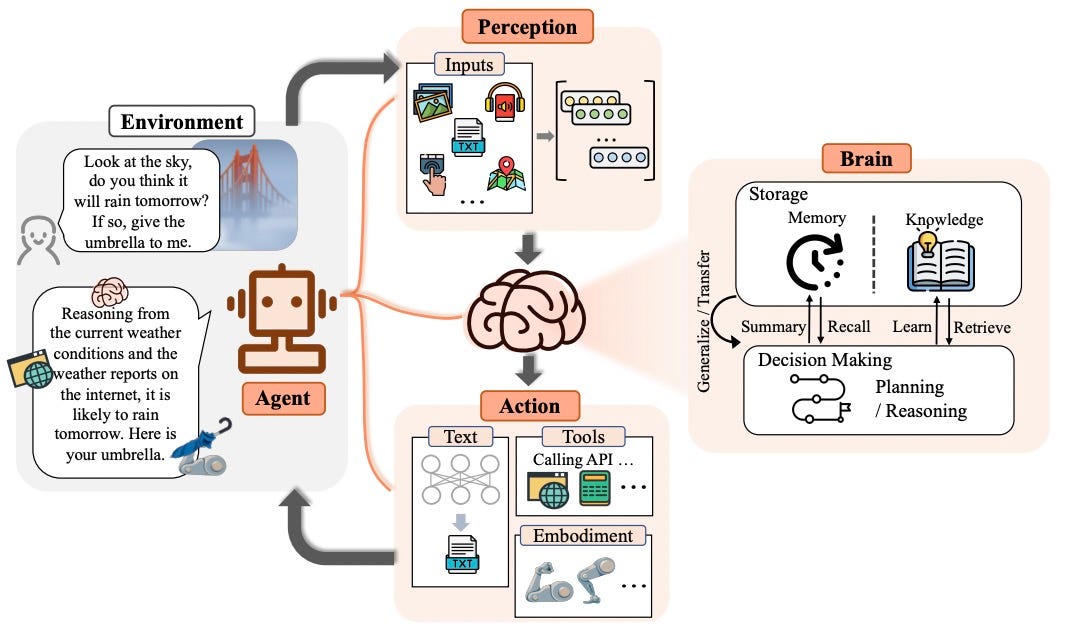
An agent is a computer program that acts on behalf of a user or another program. It is designed to automate tasks, make decisions, and execute actions without requiring direct human intervention. Agents are characterized by their ability to perceive the environment, process information, and respond appropriately to achieve specific goals.
Key Characteristics of Agents
- Autonomy: Agents operate independently, making decisions without direct input from users.
- Reactivity: They can perceive their environment and respond in real-time to changes and stimuli.
- Adaptability: Agents learn from their experiences and improve their performance over time.
- Goal-Oriented: They are designed to achieve specific objectives or complete tasks.
Types of Agents
Agents can be classified into various categories based on their functionalities and applications:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents act solely on the basis of the current percept, ignoring the rest of the percept history. These agents function by selecting actions based on the current situation, often using condition-action rules. While they are efficient in simple environments, they struggle in complex scenarios due to their lack of memory and learning capabilities.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents maintain an internal state that tracks aspects of the world that are not immediately perceivable. This internal state allows them to handle more complex situations by considering the history of percepts.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents act to achieve specific goals. They use information about the current state of the environment to choose actions that bring them closer to their desired objectives. These agents often incorporate planning algorithms to determine the best course of action.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents aim to maximize a utility function, which quantifies the degree of satisfaction or happiness resulting from different world states. They not only consider the achievement of goals but also evaluate the desirability of outcomes, allowing for more nuanced decision-making.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents have the ability to improve their performance over time by learning from their experiences. They consist of four main components: the learning element, the performance element, the critic, and the problem generator. These components work together to enhance the agent's capability to make informed decisions.
Applications of Agents
Agents have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
1. Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are prime examples of agents. They perform tasks such as setting reminders, answering queries, and controlling smart home devices, all while learning user preferences to provide personalized experiences.
2. E-commerce
In e-commerce, agents are used to recommend products, manage inventory, and optimize pricing strategies. They analyze consumer behavior and market trends to suggest products that align with customer preferences, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
3. Finance
In the finance sector, agents are employed for algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and risk management. They analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to make informed trading decisions, identify fraudulent activities, and assess potential risks.
4. Healthcare
Healthcare agents assist in diagnosing diseases, managing patient records, and delivering personalized treatment plans. They utilize medical data and machine learning algorithms to provide accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
5. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely on agents to navigate roads, recognize traffic signals, and make real-time driving decisions. These agents process data from sensors and cameras to ensure safe and efficient transportation.
The Future of Agents
As technology continues to advance, the role of agents is expected to expand further. Here are some trends shaping the future of agents:
1. Enhanced Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Advancements in NLP will enable agents to understand and respond to human language with greater accuracy and nuance. This will enhance their ability to interact seamlessly with users, making them more intuitive and user-friendly.
2. Improved Machine Learning Algorithms
As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, agents will be able to learn from larger datasets and make more accurate predictions. This will enhance their decision-making capabilities and expand their range of applications.
3. Increased Personalization
Agents will continue to evolve in their ability to provide personalized experiences. By analyzing user behavior and preferences, agents will tailor their actions and recommendations to meet individual needs and preferences.
4. Integration with IoT
The integration of agents with the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable them to interact with a wide range of connected devices. This will create a more interconnected and intelligent ecosystem, where agents can seamlessly manage and control smart devices.
5. Ethical and Privacy Considerations
As agents become more prevalent, ethical and privacy considerations will become increasingly important. Ensuring that agents operate ethically and protect user data will be crucial to gaining user trust and acceptance.
Conclusion
Agents are transforming the way we interact with technology, automating tasks, and enhancing decision-making processes across various industries. With advancements in AI and machine learning, agents are becoming more sophisticated, capable, and personalized. As we move into the future, agents will play an integral role in shaping the digital landscape, offering new possibilities and opportunities for innovation. Understanding the potential and implications of agents is essential for businesses and individuals seeking to harness their power and stay ahead in an increasingly automated world.