Understanding Agent AI: The Future of Intelligent Automation

Understanding Agent AI: The Future of Intelligent Automation
Published: 12 May 2025 | Focus keyword: agent
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the agent paradigm is reshaping how we interact with software and automate tasks. Powered by breakthroughs in machine learning and natural-language processing, AI agents act as tireless digital co-workers—analyzing data, making decisions, and executing actions with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
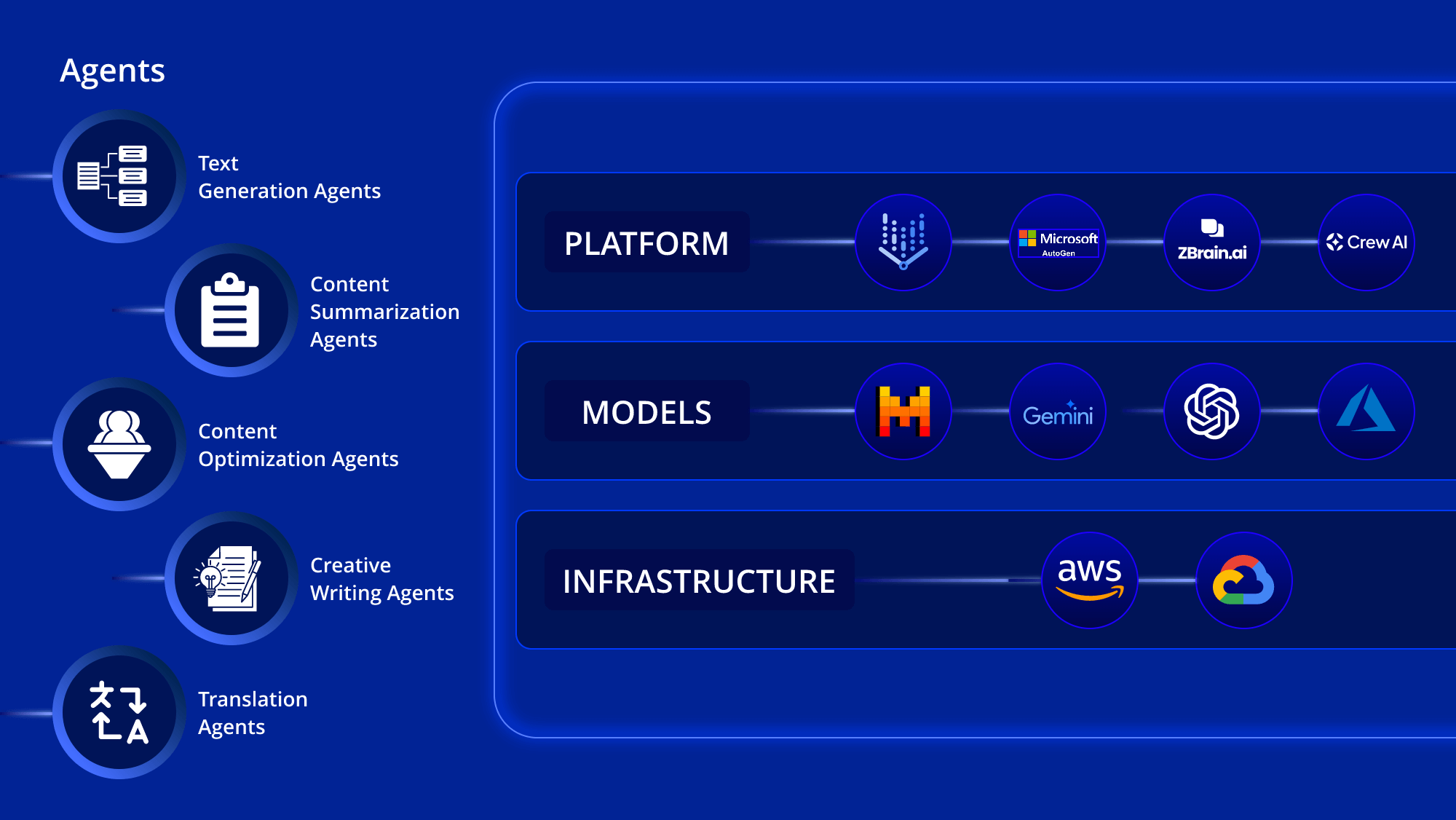
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an autonomous software program that senses its environment, reasons about goals, and acts to achieve them on a user’s behalf. Most modern agents blend three core capabilities:
- Perception – ingesting data via APIs, sensors, logs, or user prompts.
- Cognition – using machine-learning models to interpret context, predict outcomes, and plan next steps.
- Action – executing API calls, triggering workflows, or returning answers in natural language.
Key Types of Agents
- Virtual Assistants (e.g., Alexa, Siri) – voice- or text-based helpers that handle everyday tasks.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) bots – rule-driven agents that mimic clicks and keystrokes to tackle repetitive office work.
- Intelligent Personal Assistants – context-aware agents that learn user preferences and proactively surface recommendations.
- Multi-Agent Systems – swarms of specialized agents collaborating to solve complex, distributed problems (logistics, traffic control, etc.).

High-Impact Applications
1 · Customer Service
Chat-based support agents resolve routine inquiries 24 / 7, cutting ticket backlogs and boosting satisfaction.
2 · Healthcare
Diagnostic agents analyze imaging and patient records, assisting clinicians with earlier, more accurate treatment plans.
3 · Finance
Fraud-detection agents scan millions of transactions in real-time, flagging anomalies within milliseconds.
4 · E-commerce
Recommendation agents personalize product feeds, increasing average order value and retention.
Benefits at a Glance
- Efficiency – automate repetitive tasks and free humans for strategic work.
- Scalability – handle spikes in demand without proportional staffing costs.
- Accuracy – minimize human error through data-driven decision making.
- Personalization – deliver custom experiences that deepen brand loyalty.

Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite their promise, AI agents introduce concerns around data privacy, bias, transparency, and workforce disruption. Rigorous testing, responsible data governance, and clear audit trails are essential to build trust.
The Road Ahead
Future agents will tap larger multimodal models, integrate with IoT devices, and collaborate in real-time with both humans and other agents—unlocking truly adaptive digital ecosystems.
References
- LeewayHertz – “AI agents for content generation” https://www.leewayhertz.com/ai-agent-for-content-generation/
- Keploy – “Open-Source AI Agents” https://keploy.io/blog/community/top-open-source-ai-agents
- Signity Solutions – “What are AI Agents” https://www.signitysolutions.com/blog/ai-agents
© 2025 OnDemand Blog



