AI Agents: Unlocking the Future of Intelligent Automation

AI Agents: Unlocking the Future of Intelligent Automation
Date: 29 April 2025
An AI agent is an autonomous software entity that can perceive its environment, reason about it, and take actions that maximise its chance of achieving a goal. From powering virtual assistants to driving autonomous vehicles, the modern agent has become a cornerstone of digital transformation.
Types of AI Agents
- Reactive Agents – rule-based responders with no memory.
- Model-Based Agents – maintain an internal representation of the world.
- Goal-Based Agents – plan actions to accomplish explicit objectives.
- Utility-Based Agents – weigh trade-offs to maximise a utility function.
- Learning Agents – improve behaviour over time with data.
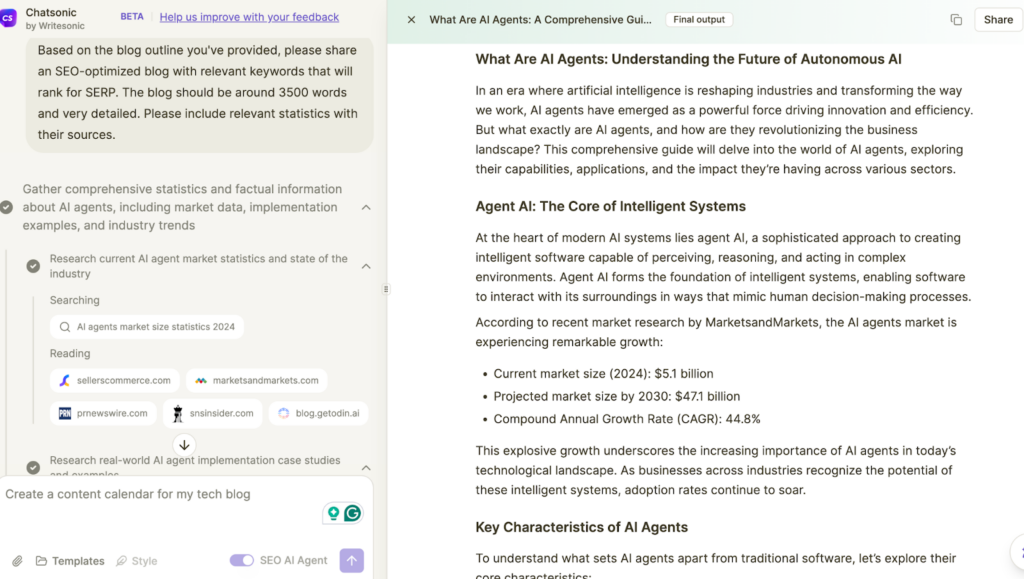
Key Architectural Components
- Perception – sensors or APIs that feed the agent data.
- Reasoning – algorithms that evaluate possible actions.
- Learning – ML techniques that refine future decisions.
- Action – the execution layer, digital or physical.
- Feedback Loop – continuous improvement cycle.
Real-World Applications
1. Cloud-Native Orchestration
Projects like Dapr introduce reusable building blocks so that any microservice can act as an intelligent agent.

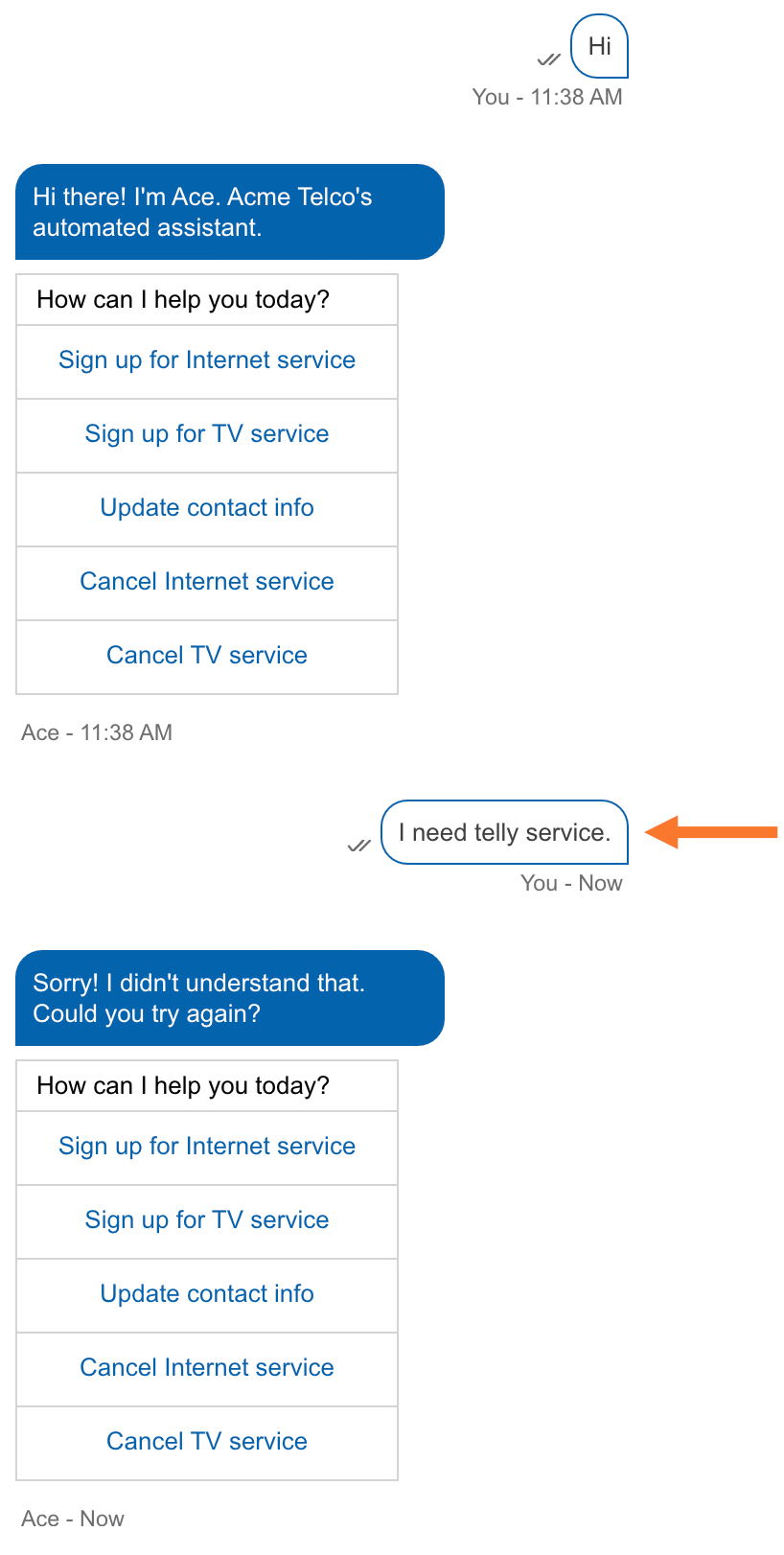
2. Conversational Routing
In customer support, routing agents triage user intent and direct queries to the right human or bot.
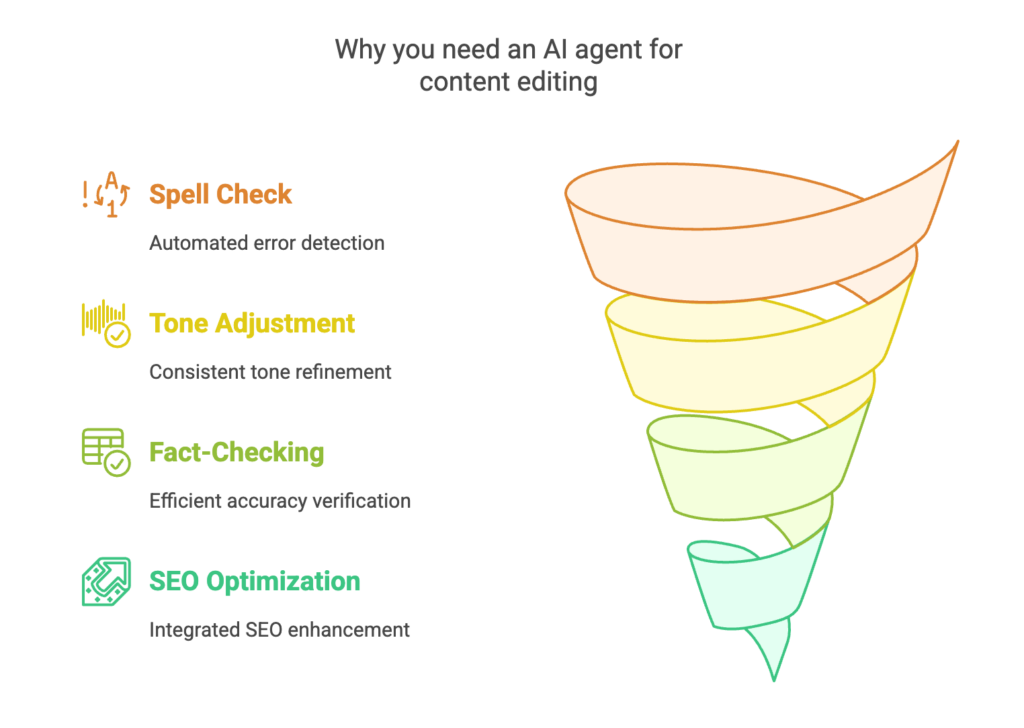
3. Editorial Automation
Editing agents scan drafts for grammar, structure, and SEO, helping writers publish faster.
Benefits of Deploying an AI Agent
- Efficiency – 24/7 operation with near-instant throughput.
- Scalability – one agent can serve thousands of users simultaneously.
- Cost Optimisation – automates repetitive tasks, lowering overhead.
- Adaptability – learning loops keep the agent relevant in dynamic environments.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Organisations must address data privacy, bias mitigation, transparency, and security when deploying any autonomous agent. A robust governance framework and continuous monitoring are non-negotiable.
The Road Ahead
With deeper integration of IoT sensors and large language models, tomorrow’s AI agent will be more context-aware, explainable, and collaborative. Businesses that invest early will gain a durable competitive advantage.
Bottom line: The AI agent is not just a tool—it’s a strategic co-worker that augments human capability and unlocks new horizons of intelligent automation.


