AI Agents: Transforming the Future of Automation

AI Agents: Transforming the Future of Automation
Keyword focus: agent
What is an AI agent?
An agent is an autonomous software entity that perceives its environment, reasons over data, and acts toward a goal without constant human supervision. Modern AI agents combine machine learning, large language models (LLMs), symbolic reasoning, and orchestration frameworks to carry out tasks from scheduling meetings to optimizing industrial supply chains.

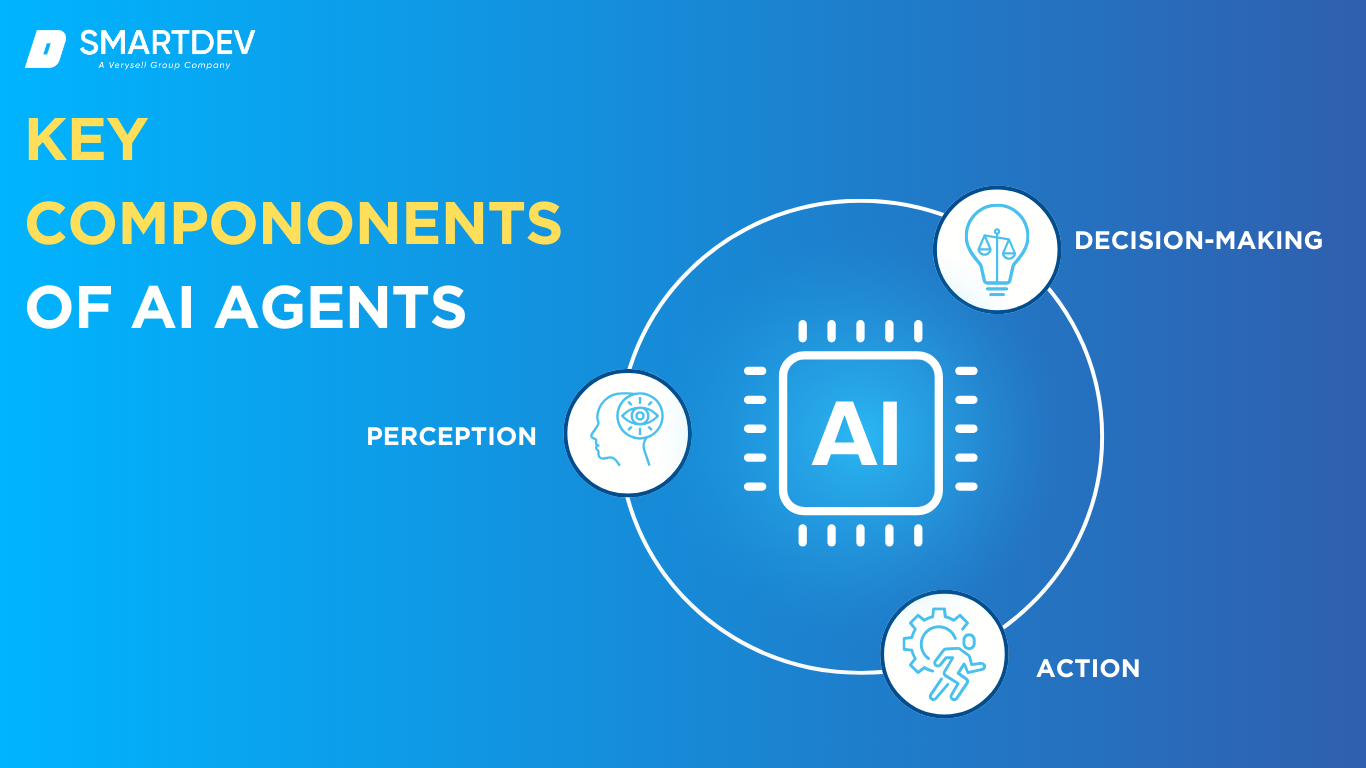
Core Capabilities of an AI agent
- Sensing: ingest structured & unstructured data in real time.
- Reasoning: build context with vector embeddings & knowledge graphs.
- Planning: break a broad goal into executable subtasks.
- Acting: call APIs, trigger RPA bots, or converse with humans.
- Learning: update policies from feedback and outcomes.
Industry Applications
1. Healthcare
Agents read radiology scans, triage patient tickets, and draft clinical notes, cutting documentation time by 45 % (Appventurez, 2025).
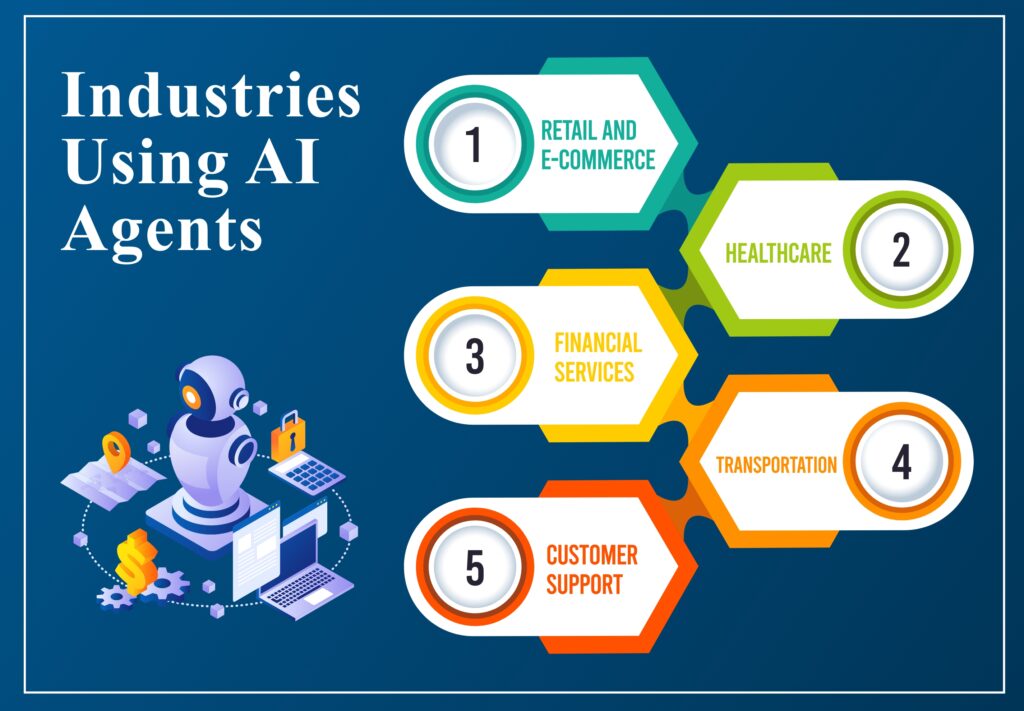
2. Manufacturing
Predictive-maintenance agents monitor vibration, temperature, and acoustic signals to pre-empt equipment failure, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 30 %.

3. Marketing & Sales
Campaign-optimization agents A/B test thousands of ad variants, driving 25 % higher conversion according to Markovate’s 2025 study.

4. Customer Service
Conversational agents resolve up to 80 % of tier-1 tickets, allowing human agents to focus on high-value interactions (Ampcome, 2024).
.png)
5. Finance
Fraud-detection agents flag anomalous transactions in milliseconds, preventing billions in losses globally each year (SmartDev, 2025).
Benefits at a Glance
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Speed | 24/7 execution with sub-second response times |
| Accuracy | Consistent adherence to rules & best practices |
| Scalability | Handle millions of requests in parallel |
| Cost | ROI often exceeds 5× within year one |
Ethical & Governance Considerations
Every agent deployment should follow three pillars:
- Transparency – explainability reports on decisions
- Fairness – continuous bias audits on training data
- Privacy – zero-trust architecture & differential logging
The Road Ahead
In 2025 and beyond, multi-agent systems will collaborate, negotiate, and self-coordinate, unlocking fully autonomous supply chains, energy grids, and research pipelines.
Key Takeaways
- The term agent refers to a self-directed AI entity that senses, thinks, and acts.
- Industries are adopting agents to boost productivity, cut costs, and enhance user experiences.
- Robust governance frameworks are essential to deploy agents responsibly.
— End of article —



