AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Automation
AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Automation
In just a few short years, the agent paradigm has shifted from a futuristic concept to an operational reality powering businesses worldwide. From self-driving supply chains to hyper-personalized marketing campaigns, AI agents now act as tireless digital coworkers that plan, reason, and act on our behalf—24/7, without fatigue. This 1,500-word guide explores how modern agents are built, where they deliver the greatest ROI, and why forward-thinking organizations are rushing to embrace them.

What Exactly Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a software entity capable of perceiving its environment, reasoning over goals, and executing actions autonomously. Unlike rule-based bots, modern agents combine large language models (LLMs), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), planning modules, and tool-calling APIs. This layered architecture enables them to learn continuously, adapt to new information, and collaborate with other systems—including fellow agents—without explicit human prompts.
Core Components of an Agentic System
Sensing & Context Fusion
Agents ingest structured and unstructured signals: CRM records, IoT telemetry, emails, voice, and more. Vector databases transform multimodal data into dense embeddings, giving the agent semantic awareness of what is happening right now.
Reasoning & Planning
By pairing chain-of-thought reasoning with symbolic planning, an agent can break vague objectives (e.g., “optimize warehouse throughput”) into step-by-step subtasks, dynamically revising its plan as new constraints emerge.
Tool Invocation
Through secure APIs, agents trigger downstream systems—ERP, marketing automation, payment rails—closing the loop between decision and action.
Memory & Learning
Long-term vector memories let an agent store outcomes, reflect on mistakes, and self-improve. Over time, the system evolves from reactive script to proactive advisor.
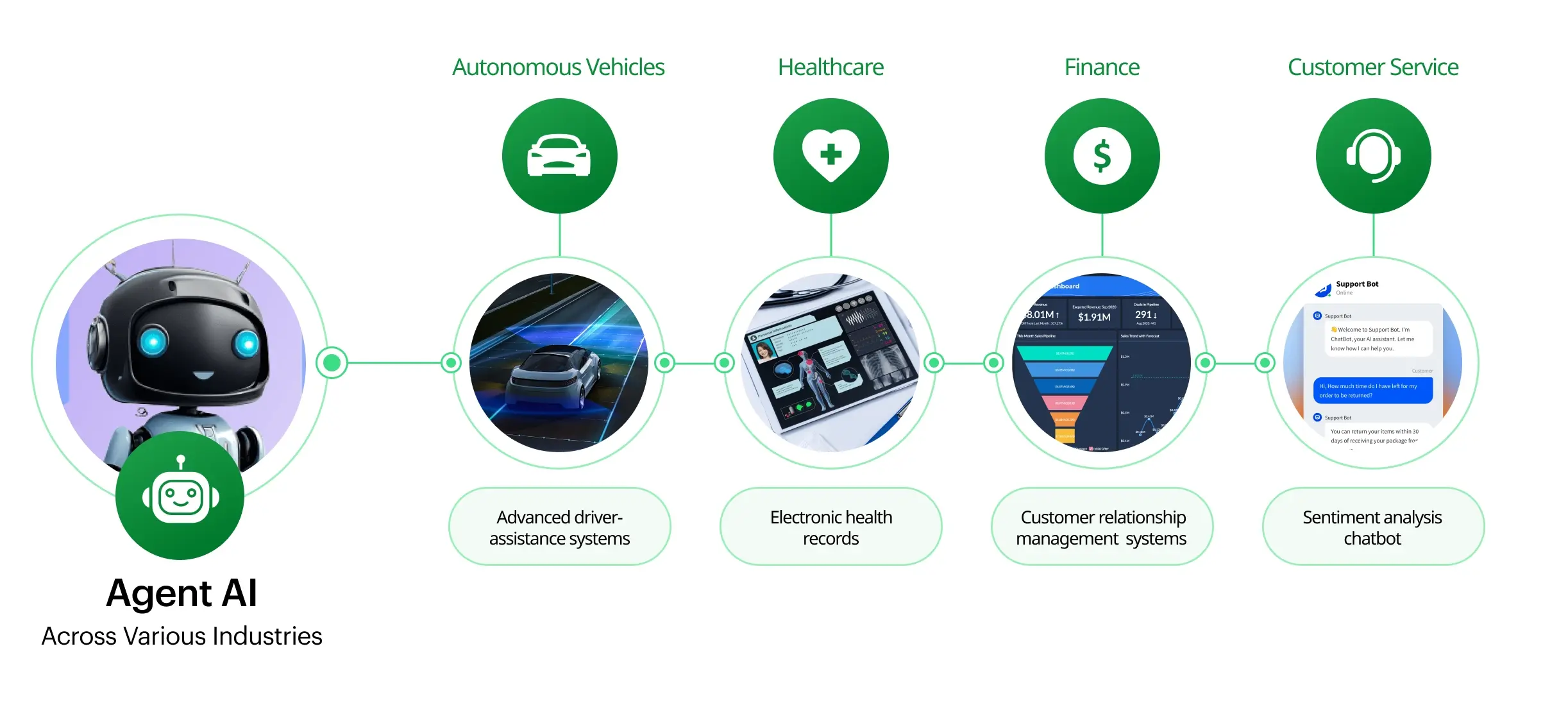
Industry Applications
1. Healthcare
Clinical triage agents analyze patient symptoms, schedule diagnostics, and surface treatment guidelines in seconds. Radiology agents pre-screen scans, flagging anomalies and reducing physician workload by up to 60 percent.
2. Finance
Fraud-detection agents monitor millions of transactions per minute, cross-referencing behavioral patterns against historical data to halt suspicious payments in near-real-time.
3. Manufacturing
Shop-floor agents adjust machine parameters, predict maintenance windows, and reorder parts automatically—slashing unplanned downtime.
4. Customer Service
Omnichannel support agents blend LLM-powered dialog, CRM history, and policy retrieval to resolve 80 percent of tickets without escalation, all while sounding distinctly human.
5. Marketing & Sales
Demand-gen agents A/B-test copy, analyze sentiment, and generate hyper-personalized nurture streams that increase conversion by double-digit percentages.
Business Benefits of Deploying an Agent
- 24/7 Productivity – Agents never sleep, ensuring round-the-clock coverage.
- Cost Efficiency – Automating rote tasks cuts labor spend by 20-40 percent.
- Decision Precision – Data-driven reasoning minimizes human error and bias.
- Scalability – New agent instances can be spawned in seconds to meet demand spikes.
- Continuous Learning – Feedback loops let agents self-optimize without costly re-engineering.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite their promise, agents are not plug-and-play silver bullets. Data privacy regulations (GDPR, HIPAA), model hallucinations, and latent bias must be mitigated through rigorous benchmarking and human-in-the-loop governance. Explainability dashboards and audit trails help stakeholders trust that an agent’s recommendations are fair and transparent.
The Road Ahead
By 2030, Gartner predicts that agent collectives—swarms of specialized agents coordinating via natural-language protocols—will manage entire business processes end-to-end. Expect tighter IoT integration, emotion-aware dialog, and self-provisioning cloud resources that scale autonomously in response to an agent’s evolving plan.
Conclusion
From boardrooms to factory floors, the rise of the AI agent signals a new era of intelligent automation. Organizations that pilot agentic workflows today will enjoy compound advantages in cost, speed, and insight tomorrow. The question is no longer whether agents will transform your industry—but how soon you will let them.



