AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Automation

AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Automation
Focus keyword: agent

Introduction
From virtual assistants in our pockets to autonomous robots in smart factories, the agent paradigm is redefining how software interacts with the world. An AI agent is an autonomous program that observes its environment, reasons about goals, and acts—often without direct human intervention. In 2025, a wave of breakthroughs in large-language-model tooling, edge computing, and cloud orchestration has pushed these agents into mainstream adoption.
What Is an AI Agent?
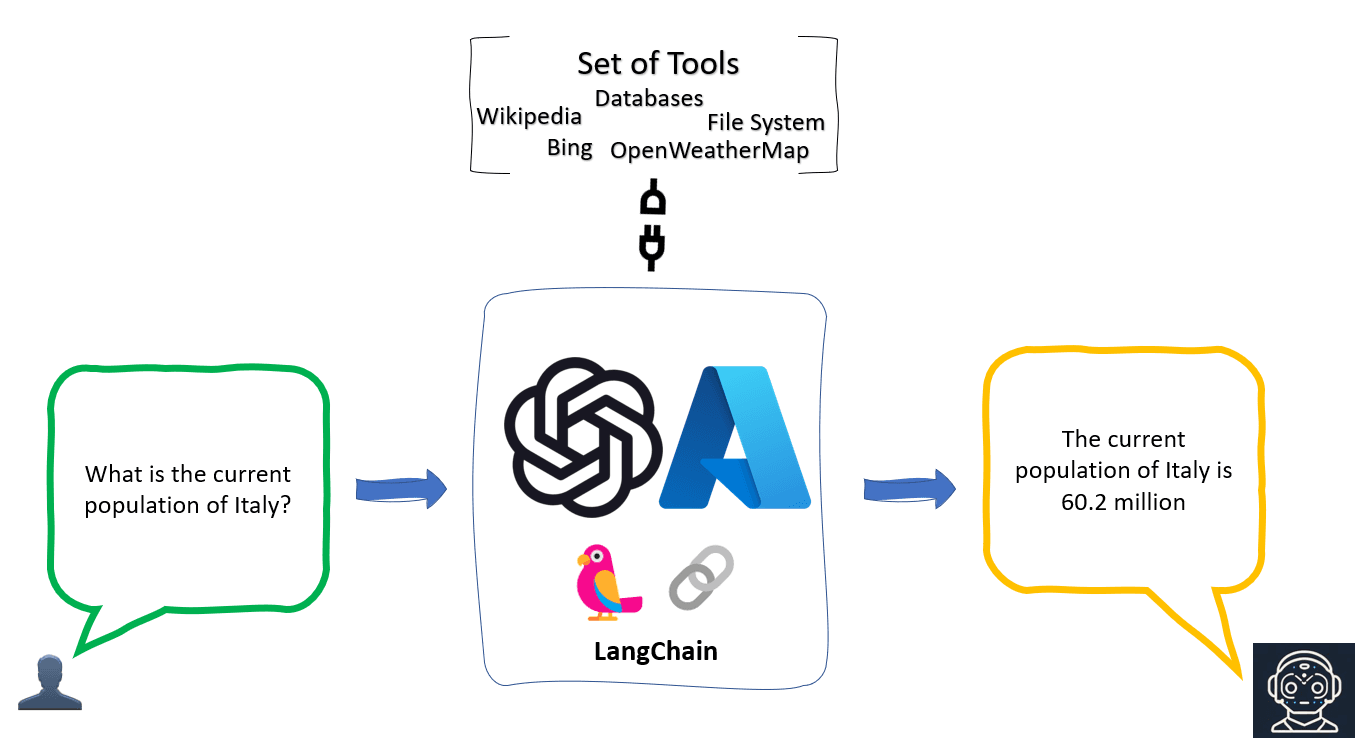
At its core, an AI agent comprises a perception module, a decision-making engine, and an actuation layer. The perception module ingests data (text, images, sensor streams). The internal engine leverages machine-learning models to plan. Finally, the actuation layer executes tasks—writing code, sending emails, moving a robotic arm, or triggering APIs—until the goal is met.
Core Components
- Memory – short- and long-term stores that help the agent learn from past interactions.
- Reasoning – algorithms (planning, reinforcement learning) used to decide next actions.
- Tooling – external plugins or APIs that extend the agent’s capabilities, e.g., web search or database access.
- Feedback loop – continuous evaluation that helps the agent self-improve.
Industry Use-Cases
1. Healthcare & Diagnostics

AI agents triage radiology images, flag anomalies in real time, and schedule follow-up consultations—cutting diagnosis time by up to 60% (SoftLabsGroup, 2025).
2. Content Marketing
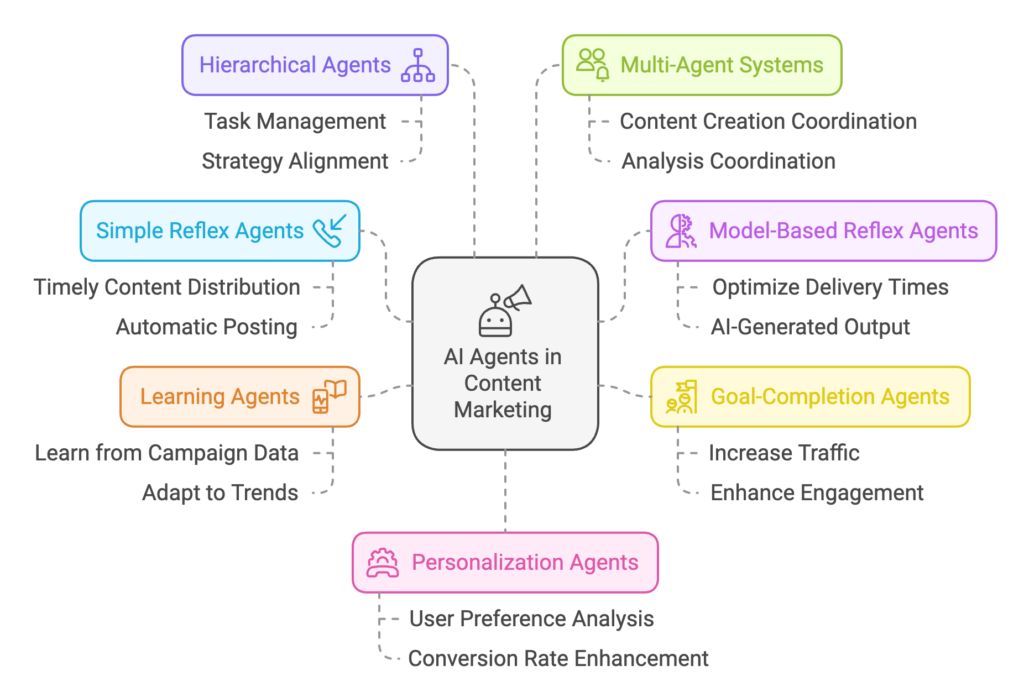
Marketers deploy writing agents to research keywords, draft blogs, and A/B-test headlines—boosting ROI while slashing production costs.
3. Customer Service & Chatbots

Enterprises integrate multilingual chat agents that understand intent, retrieve knowledge-base answers, and escalate complex tickets to humans when needed.
4. Financial Forecasting

Trading desks enlist portfolio-management agents that monitor macro news, adjust risk exposure, and execute high-frequency trades within milliseconds.
5. Software Development & DevOps
Autonomous coding agents draft boilerplate, generate unit tests, and open pull requests, accelerating release cycles.
Benefits of Deploying an AI Agent
- 24/7 Productivity – agents never sleep, ensuring continuous operation.
- Scalability – easily spin up more instances during peak demand.
- Error Reduction – statistical learning reduces human slip-ups.
- Cost Savings – automation frees human experts to tackle higher-value tasks.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Bias in training data, privacy regulation (GDPR/CCPA), and explainability remain top concerns. Governance frameworks and human-in-the-loop reviews can mitigate risk.
Future Outlook
Nvidia’s Jensen Huang predicts 2025 will be “the year of the AI agents.” Expect deeper Internet-of-Things integration, on-device inference, and collaborative multi-agent systems tackling complex goals together.
Conclusion
An AI agent represents the next evolution in intelligent automation—capable of perception, reasoning, and action. Organizations that adopt these systems today will gain a compounding competitive advantage in efficiency, insight, and innovation.
References
- SoftLabsGroup – “AI Agents: What They Actually Do (Types + Future Trends)” (2025)
- Writesonic – “AI Agents in Content Marketing” (2025)
- Signity Solutions – “What Are AI Agents: Types, Benefits, Applications” (2024)
- International Banker – “Will 2025 Be the Year of the AI Agents?” (2025)
- SoluteLabs – “What Is an AI Agent? Your Ultimate Guide” (2024)



