AI Agents: Revolutionizing Automation Across Industries

AI Agents: Revolutionizing Automation Across Industries
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are redefining how modern enterprises operate, automating complex workflows, accelerating decision-making, and unlocking unprecedented efficiency. This in-depth guide explores what an AI agent is, how each type functions, key applications, and why forward-thinking organizations are rapidly adopting agent-based solutions.
What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a software entity that perceives its environment, reasons about the best course of action, and autonomously performs tasks to achieve specific goals. Equipped with sensors (data inputs) and actuators (outputs), an agent continuously learns from feedback, adapting its behavior in real time.
Core Types of AI Agents
- Reactive Agents – stimulus-response systems with no internal memory.
- Deliberative Agents – maintain a world model and plan multi-step actions.
- Hybrid Agents – merge reactive speed with deliberative reasoning.
- Learning Agents – improve decisions through machine-learning feedback.
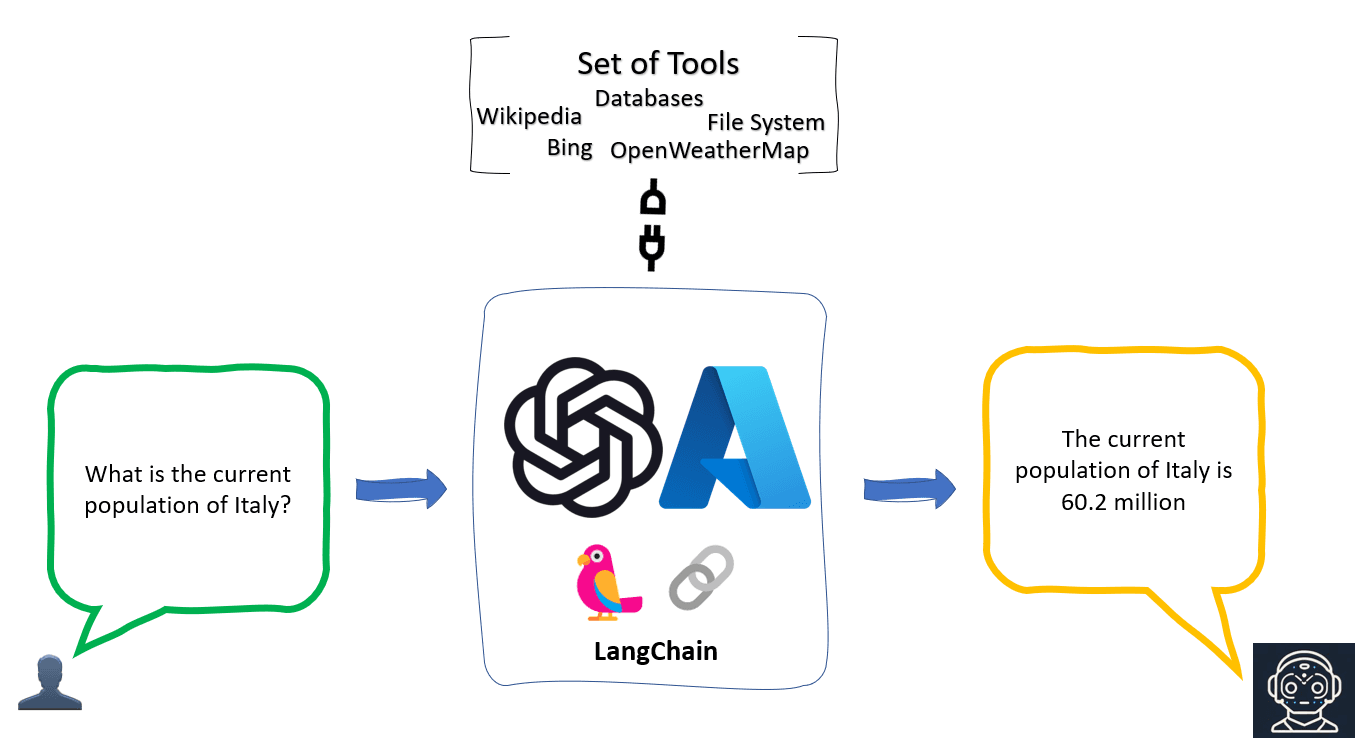
Key Applications of AI Agents
1. Healthcare
Diagnostic agents analyze imaging data, while triage chatbots improve patient engagement and reduce administrative burden.
2. Finance
Trading agents execute millisecond-level transactions, and fraud-detection agents flag anomalies across millions of daily payments.
3. Customer Service
Conversational agents provide 24/7 support, resolving repetitive queries and elevating customer satisfaction.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
Navigation agents fuse sensor data to drive, brake, and steer safely in complex environments.
5. Smart Homes & IoT
Context-aware agents optimize energy usage, security, and entertainment based on resident behavior.

Technology Stack Behind AI Agents
- Machine Learning – supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning drive adaptation.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – enables human-agent dialog.
- Computer Vision – processes images and video streams.
- Robotics – couples digital reasoning with physical actuation.
Benefits of Deploying AI Agents
- Efficiency – agents complete tasks faster with fewer errors.
- Scalability – manage millions of events without extra staff.
- 24/7 Availability – continuous operation without fatigue.
- Cost Reduction – automation lowers operational expenses.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
- Data Privacy – securing sensitive user data processed by agents.
- Bias & Fairness – ensuring training data does not encode discrimination.
- Transparency – explainable-AI methods clarify how an agent reaches decisions.
- Job Displacement – balancing automation benefits with workforce upskilling.

The Future of AI Agents
Emerging trends include tighter IoT integration, human-AI co-creation, ultra-personalized assistant agents, and stricter governance frameworks that promote fairness, accountability, and transparency. Organizations embracing the agent paradigm today will gain a decisive competitive edge tomorrow.
Conclusion
From healthcare diagnostics to autonomous mobility, the modern agent is no longer science fiction—it is an operational necessity. By strategically deploying AI agents, companies can unlock scalable growth, streamline decision processes, and deliver superior customer value.